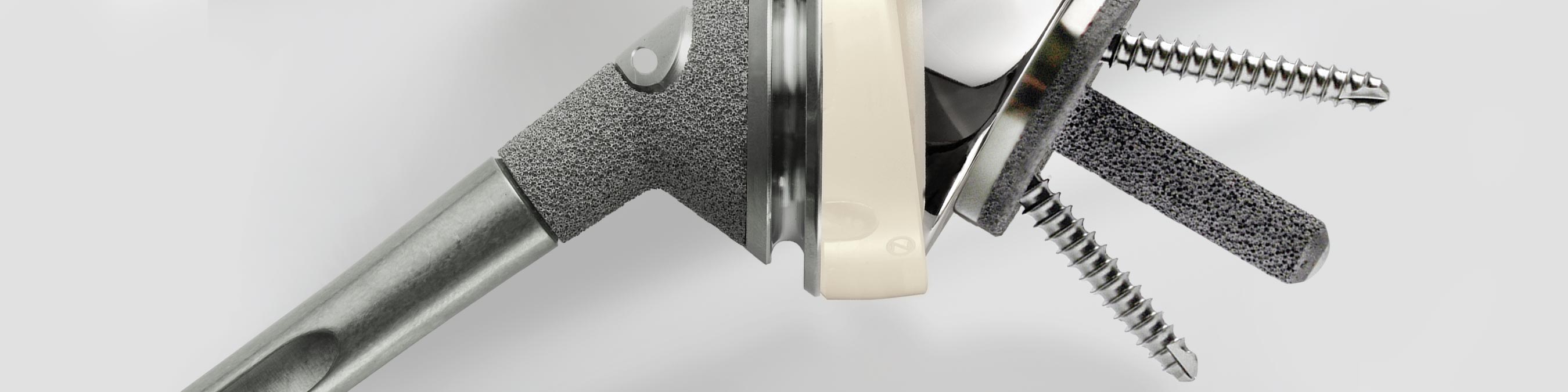
Zimmer Biomet’s Trabecular MetalTM Reverse Shoulder System presents a comprehensive solution to meet the demands put on reverse shoulder systems.1,2 These objectives include: returning cuff-deficient patients to simple activities of daily living, optimizing range of motion in the face of glenoid erosion, and ensuring tuberosity repair in complex fractures. Our Trabecular Metal base plate provides superior glenoid stability1 while the 60 degree humeral components reduce the likelihood of scapular notching.2,3
Trabecular Metal™ Reverse Shoulder System
Optimize patient outcomes across a broad range of indications


The Trabecular Metal base plate provides proven fixation and stability3
- Trabecular Metal material supports vascularization and biologic in-growth4-7
- Greater screw engagement and less bone removal than convex base plate designs8
- Center post lengths up to 30mm maximize bony engagement to minimize base plate micromotion
- Center of rotation (COR) lateral offset counters glenoid erosion2
- Personalized glenoid component planning, sizing and positioning when used with Zimmer Biomet PSI Shoulder

Reduced likelihood of scapular notching6-8
- Less than 1% grade 3 and 4 notching at 16 months. Other studies have reported 6% or more2,10,11
- Glenosphere COR lateral offset and inferior overhang reduce probability of impingement with the scapular pillar2
- Humeral component angle of 150° helps provide greater clearance during adduction versus a “Grammont” prosthesis2

Trabecular Metal Reverse Humeral Stem facilitates strong fixation, healing, and enhanced range of motion
- 7 years of clinical history with over 32,000 global implantations
- Trabecular Metal material’s scaffold facilitates vascularization and biologic in-growth1-4
- High coefficient of friction between Trabecular Metal material and cancellous bone to enhance tuberosity fixation in 3- and 4-part fractures
- Extensive humeral liner and spacer combinations, ranging between +0mm and +18mm, to enable proper deltoid tensioning
- Precise retroversion control optimizes subscapularis and teres minor tension, to enhance internal and external rotation

Non-Porous Humeral Stem portfolio designed to precisely match a range of humeral canal sizes12
- 6 and 8mm stems to accommodate the smaller patients
- 200mm stems to facilitate revision from total shoulder to reverse shoulder arthroplasty
- Intraoperative flexibility between Non-Porous Reverse and Trabecular Metal Reverse humeral stems utilizing shared instrumentation

- Chalmers et al. Reverse total shoulder arthroplasty for acute proximal humeral fracture: comparison to open reduction–internal fixation and hemiarthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 2014;23:197-204.
- Kempton et al. A radiographic analysis of the effects of prosthesis design on scapular notching following reverse total shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 2011;20:571-576.
- Mroczkowski MS, Wiley R. Initial Fixation of the Trabecular Metal Reverse Shoulder Glenoid Base Plate Implant. 2008.
- Bobyn JD, et al. Characteristics of bone ingrowth and interface mechanics of a new porous tantalum biomaterial. JBJS 1999;81-B:907-914.
- Bobyn JD, et al. Characterization of a new porous tantalum biomaterial for reconstructive orthopaedics. Scientific Exhibition: 66th Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons; 1999; Anaheim, CA.
- J Musculoskel Res. 1999;3:245-251.
- Medlin DJ, et al. Metallurgical characterization of a porous tantalum biomaterial (Trabecular Metal™) for orthopaedic implant applications. Presentation, Materials & Processes for Medical Devices Conference, Anaheim, CA, 2003.
- James et al. Does glenoid baseplate geometry affect its fixation in reverse shoulder arthroplasty? J Shoulder Elbow Surg 2012;21:917-924.
- Harman M, Frankle M, Vasey M, Banks S. Initial glenoid component fixation in “reverse” total shoulder arthroplasty: a biomechanical evaluation. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 2005;14:162S-167S.
- Levigne et al. Scapular notching in reverse shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 2008;17:925-935.
- Simovitch et al. Predictors of Scapular Notching in Patients Managed with the Delta III Reverse Total Shoulder Replacement. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 2007;89:588-600.
- Robertson et al. Three-Dimensional Analysis of the Proximal Part of the Humerus Relevance to Arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg 2000;82A:1594:1602.

Legal Manufacturer:
Zimmer, Inc
1800 West Center Street
Warsaw, Indiana
46580 USA